The goal of caretForecast is to provide tools for forecasting time series data using various machine learning algorithms.
The CRAN version with:
install.packages("caretForecast")The development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("Akai01/caretForecast")These are basic examples which shows you how to solve common problems with different ML models.
library(caretForecast)
#> Registered S3 method overwritten by 'quantmod':
#> method from
#> as.zoo.data.frame zoo
# Forecasting with glmboost
data(retail_wide, package = "caretForecast")
i <- 8
dtlist <- caretForecast::split_ts(retail_wide[,i], test_size = 12)
training_data <- dtlist$train
testing_data <- dtlist$test
fit <- ARml(training_data, max_lag = 12, caret_method = "glmboost",
verbose = FALSE)
#> Loading required package: lattice
#> Loading required package: ggplot2
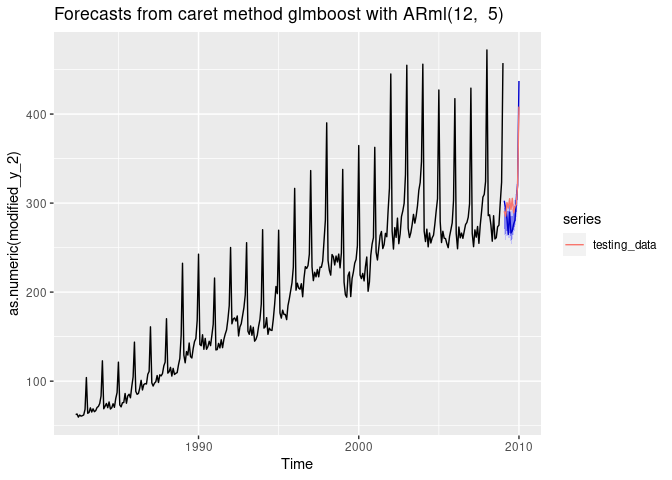
forecast(fit, h = length(testing_data), level = c(80,95), PI = TRUE)-> fc
accuracy(fc, testing_data)
#> ME RMSE MAE MPE MAPE MASE
#> Training set 0.8868074 16.39661 11.65025 -0.3620986 5.702257 0.7559694
#> Test set 8.3976171 20.15546 17.20306 3.0153042 5.572722 1.1162843
#> ACF1 Theil's U
#> Training set 0.5707204 NA
#> Test set 0.3971016 0.7547318
autoplot(fc) +
autolayer(testing_data, series = "testing_data")
## NOTE : Promotions, holidays, and other external variables can be added in the model via xreg argument. Please look at the documentation of ARml.
# Forecasting with cubist regression
i <- 9
data(retail_wide, package = "caretForecast")
dtlist <- caretForecast::split_ts(retail_wide[,i], test_size = 12)
training_data <- dtlist$train
testing_data <- dtlist$test
fit <- ARml(training_data, max_lag = 12, caret_method = "cubist",
verbose = FALSE)
forecast(fit, h = length(testing_data), level = c(80,95), PI = TRUE)-> fc
accuracy(fc, testing_data)
#> ME RMSE MAE MPE MAPE MASE
#> Training set 0.3452345 16.39877 12.22406 -0.08475644 2.533889 0.4073634
#> Test set 2.5562312 14.21461 12.39887 0.24907619 1.592606 0.4131888
#> ACF1 Theil's U
#> Training set 0.2309758 NA
#> Test set -0.1450719 0.1701567
autoplot(fc) +
autolayer(testing_data, series = "testing_data")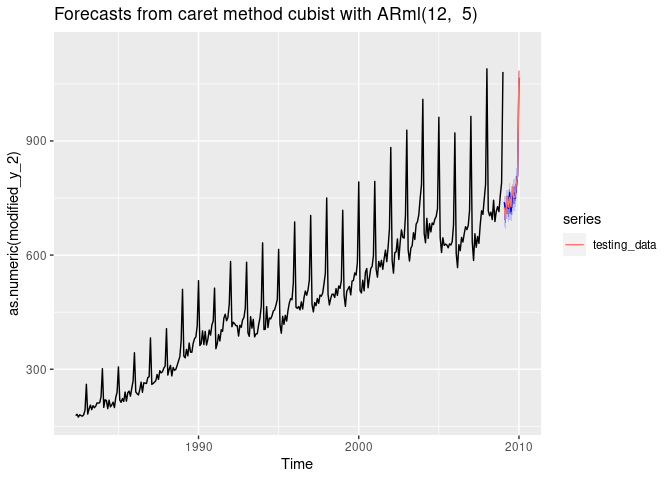
# Forecasting using Support Vector Machines with Linear Kernel
data(retail_wide, package = "caretForecast")
i <- 9
dtlist <- caretForecast::split_ts(retail_wide[,i], test_size = 12)
training_data <- dtlist$train
testing_data <- dtlist$test
fit <- ARml(training_data, max_lag = 12, caret_method = "svmLinear2",
verbose = FALSE, pre_process = c("scale", "center"))
forecast(fit, h = length(testing_data), level = c(80,95), PI = TRUE)-> fc
accuracy(fc, testing_data)
#> ME RMSE MAE MPE MAPE MASE
#> Training set 1.086666 15.67422 11.87520 0.06663619 2.497392 0.3957375
#> Test set 10.671509 16.75893 12.72986 1.33830385 1.611293 0.4242188
#> ACF1 Theil's U
#> Training set 0.09739853 NA
#> Test set -0.27328009 0.2062128
autoplot(fc) +
autolayer(testing_data, series = "testing_data")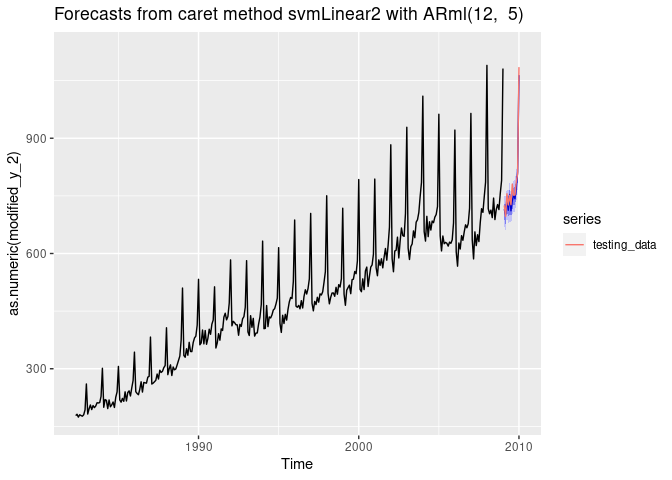
get_var_imp(fc)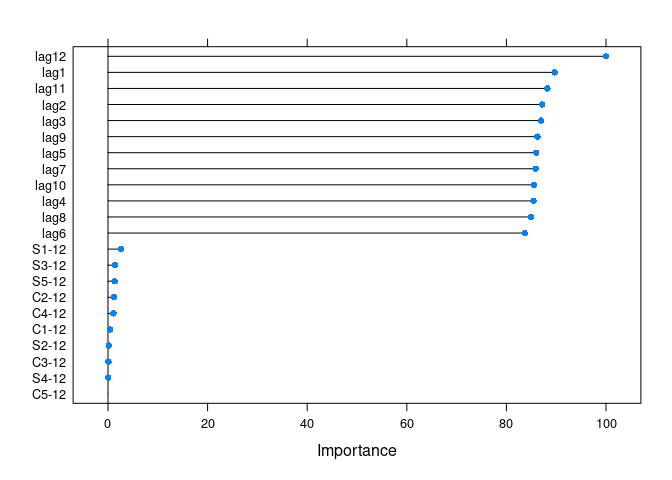
get_var_imp(fc, plot = F)
#> loess r-squared variable importance
#>
#> only 20 most important variables shown (out of 22)
#>
#> Overall
#> lag12 100.00000
#> lag1 89.70809
#> lag11 88.21434
#> lag2 87.15896
#> lag3 86.95035
#> lag9 86.22539
#> lag5 85.98743
#> lag7 85.86392
#> lag10 85.56408
#> lag4 85.44561
#> lag8 84.95210
#> lag6 83.66422
#> S1-12 2.62893
#> S3-12 1.38199
#> S5-12 1.32829
#> C2-12 1.21307
#> C4-12 1.09981
#> C1-12 0.44682
#> S2-12 0.14723
#> C3-12 0.09562
# Forecasting using Ridge Regression
data(retail_wide, package = "caretForecast")
i <- 8
dtlist <- caretForecast::split_ts(retail_wide[,i], test_size = 12)
training_data <- dtlist$train
testing_data <- dtlist$test
fit <- ARml(training_data, max_lag = 12, caret_method = "ridge",
verbose = FALSE)
forecast(fit, h = length(testing_data), level = c(80,95), PI = TRUE)-> fc
accuracy(fc, testing_data)
#> ME RMSE MAE MPE MAPE MASE
#> Training set 0.1414756 8.88367 6.44208 -0.0953757 3.126316 0.4180182
#> Test set 0.9965672 17.71459 13.30744 0.7019753 4.092068 0.8635023
#> ACF1 Theil's U
#> Training set 0.004518837 NA
#> Test set 0.389409945 0.6513039
autoplot(fc) +
autolayer(testing_data, series = "testing_data")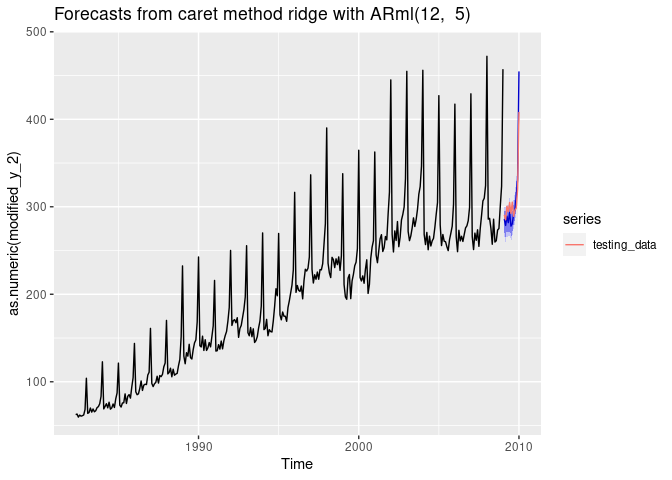
get_var_imp(fc)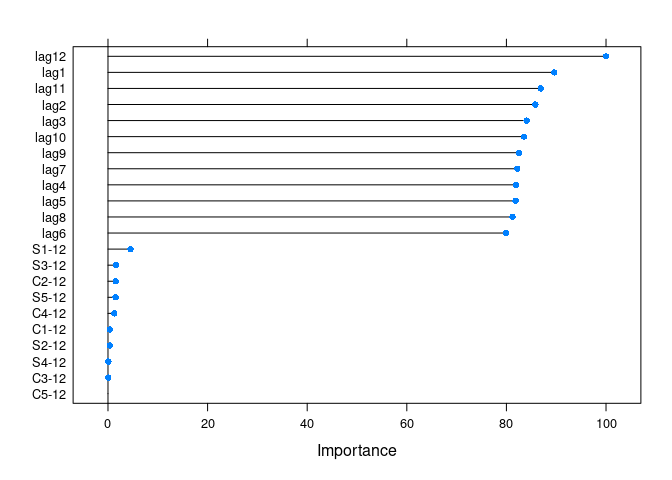
get_var_imp(fc, plot = F)
#> loess r-squared variable importance
#>
#> only 20 most important variables shown (out of 22)
#>
#> Overall
#> lag12 100.00000
#> lag1 89.57697
#> lag11 86.89260
#> lag2 85.81967
#> lag3 84.07269
#> lag10 83.53358
#> lag9 82.52774
#> lag7 82.18917
#> lag4 81.93730
#> lag5 81.85290
#> lag8 81.22696
#> lag6 79.96364
#> S1-12 4.51371
#> S3-12 1.59063
#> C2-12 1.54661
#> S5-12 1.53004
#> C4-12 1.24044
#> C1-12 0.38784
#> S2-12 0.35446
#> S4-12 0.07244