lrren
|
Main function. Estimate an ecological niche using the spatial relative risk function and predict its location in geographic space.
|
perlrren
|
Sensitivity analysis for lrren whereby observation locations are spatially perturbed (“jittered”) with specified radii, iteratively.
|
plot_obs
|
Display multiple plots of the estimated ecological niche from lrren output.
|
plot_predict
|
Display multiple plots of the predicted spatial distribution from lrren output.
|
plot_cv
|
Display multiple plots of internal k-fold cross-validation diagnostics from lrren output.
|
plot_perturb
|
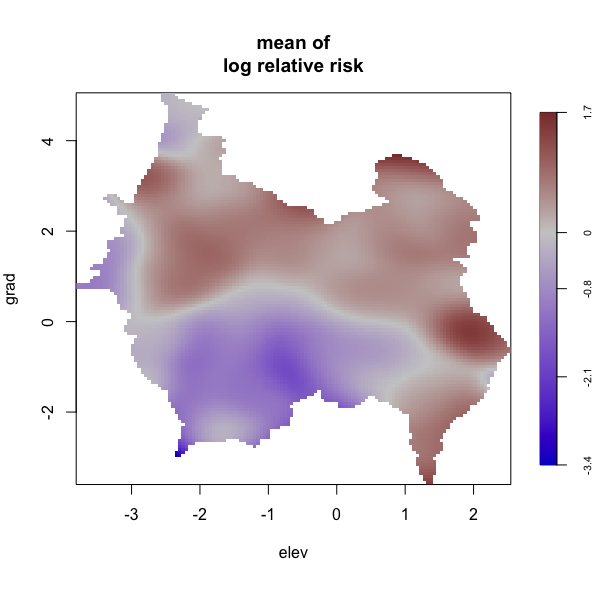
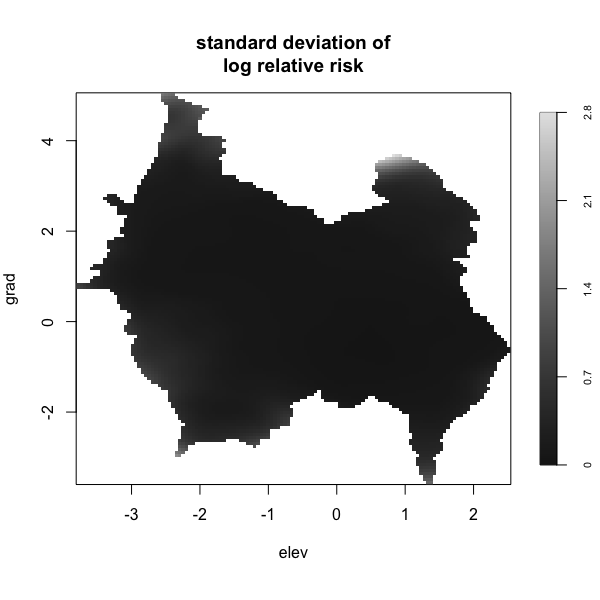
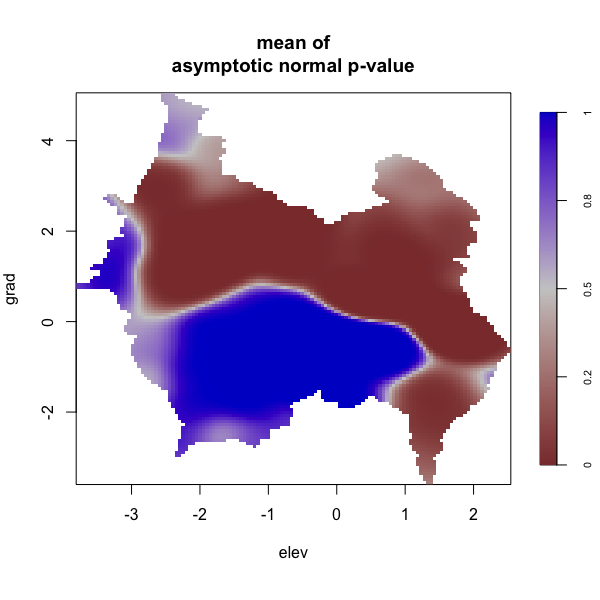
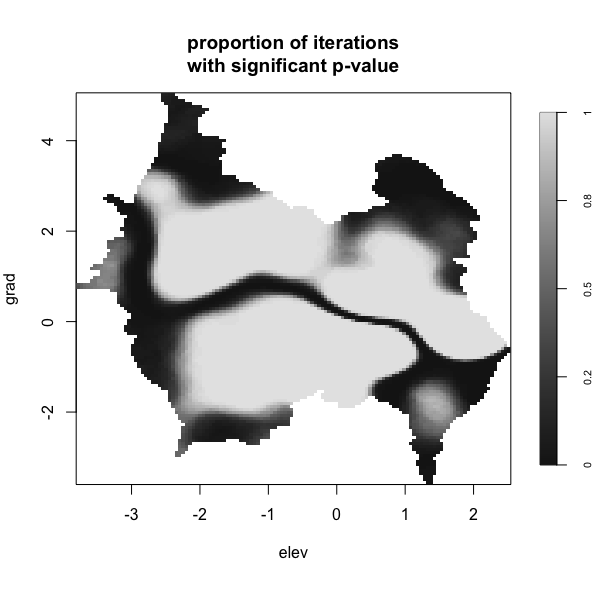
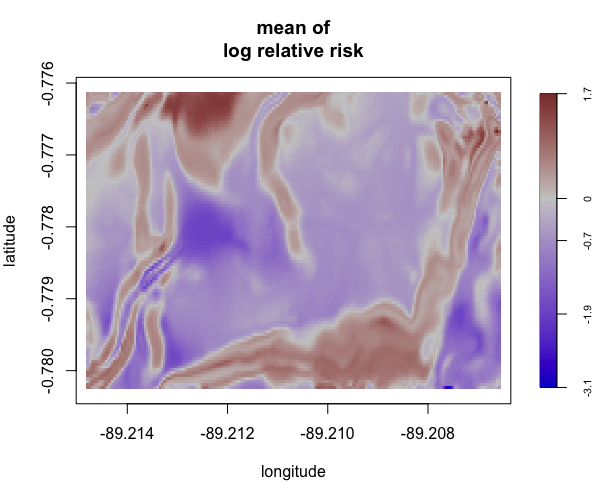
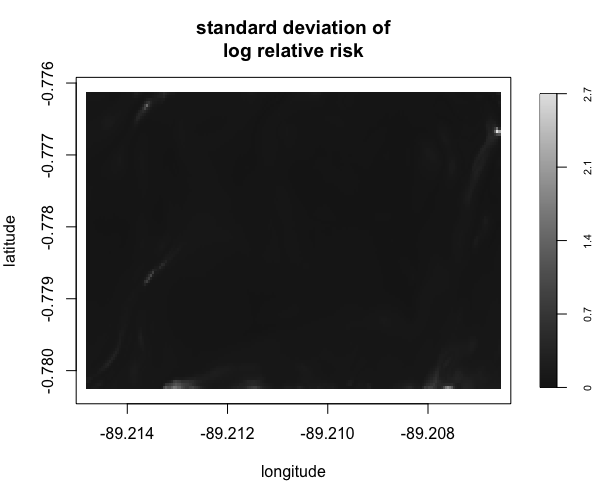
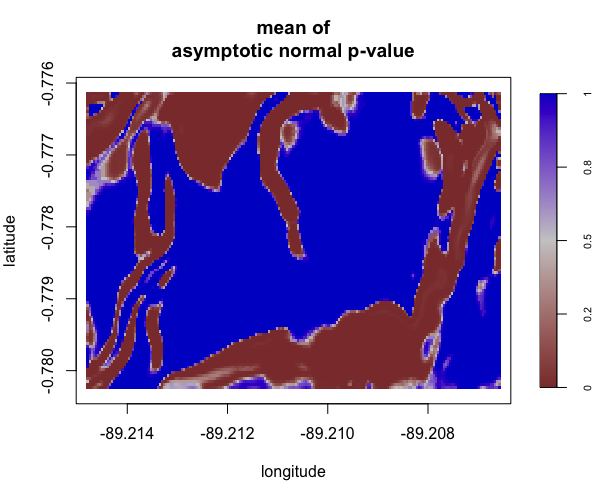
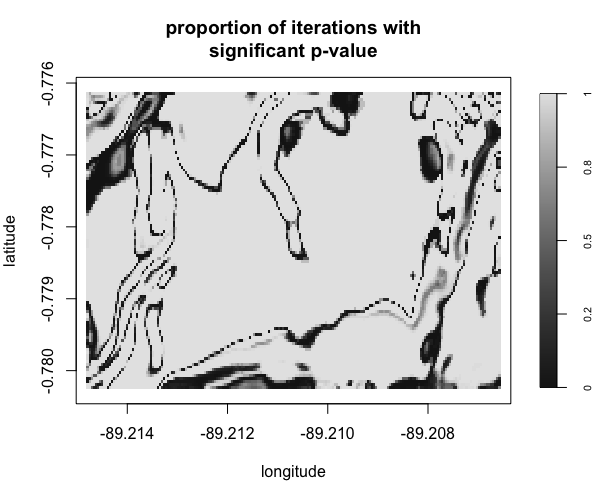
Display multiple plots of output from perlrren including prediced spatial distribution of the summary statistics.
|
div_plot
|
Called within plot_obs, plot_predict, and plot_perturb, provides functionality for basic visualization of surfaces with diverging color palettes.
|
seq_plot
|
Called within plot_perturb, provides functionality for basic visualization of surfaces with sequential color palettes.
|
pval_correct
|
Called within lrren and perlrren, calculates various multiple testing corrections for the alpha level.
|
Authors
- Ian D. Buller - Environmental Health Sciences, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia. - GitHub
See also the list of contributors who participated in this package, including:
- Lance A. Waller - Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia. - GitHub
Usage
For the lrren() function
set.seed(1234) # for reproducibility
# ------------------ #
# Necessary packages #
# ------------------ #
library(envi)
library(raster)
library(spatstat.data)
library(spatstat.geom)
library(spatstat.random)
# -------------- #
# Prepare inputs #
# -------------- #
# Using the 'bei' and 'bei.extra' data within {spatstat.data}
# Environmental Covariates
elev <- spatstat.data::bei.extra[[1]]
grad <- spatstat.data::bei.extra[[2]]
elev$v <- scale(elev)
grad$v <- scale(grad)
elev_raster <- raster::raster(elev)
grad_raster <- raster::raster(grad)
# Presence data
presence <- spatstat.data::bei
spatstat.geom::marks(presence) <- data.frame("presence" = rep(1, presence$n),
"lon" = presence$x,
"lat" = presence$y)
spatstat.geom::marks(presence)$elev <- elev[presence]
spatstat.geom::marks(presence)$grad <- grad[presence]
# (Pseudo-)Absence data
absence <- spatstat.random::rpoispp(0.008, win = elev)
spatstat.geom::marks(absence) <- data.frame("presence" = rep(0, absence$n),
"lon" = absence$x,
"lat" = absence$y)
spatstat.geom::marks(absence)$elev <- elev[absence]
spatstat.geom::marks(absence)$grad <- grad[absence]
# Combine
obs_locs <- spatstat.geom::superimpose(presence, absence, check = FALSE)
obs_locs <- spatstat.geom::marks(obs_locs)
obs_locs$id <- seq(1, nrow(obs_locs), 1)
obs_locs <- obs_locs[ , c(6, 2, 3, 1, 4, 5)]
# Prediction Data
predict_locs <- data.frame(raster::rasterToPoints(elev_raster))
predict_locs$layer2 <- raster::extract(grad_raster, predict_locs[, 1:2])
# ----------- #
# Run lrren() #
# ----------- #
test1 <- envi::lrren(obs_locs = obs_locs,
predict_locs = predict_locs,
predict = TRUE,
verbose = TRUE,
cv = TRUE)
# -------------- #
# Run plot_obs() #
# -------------- #
envi::plot_obs(test1)
# ------------------ #
# Run plot_predict() #
# ------------------ #
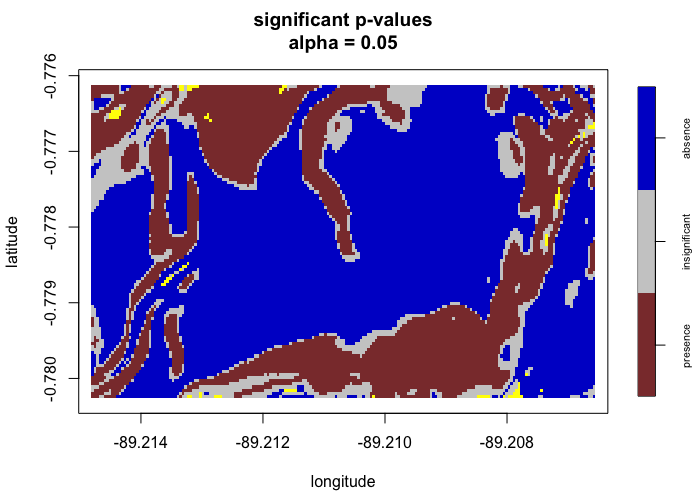
envi::plot_predict(test1,
cref0 = "EPSG:5472",
cref1 = "EPSG:4326")
# ------------- #
# Run plot_cv() #
# ------------- #
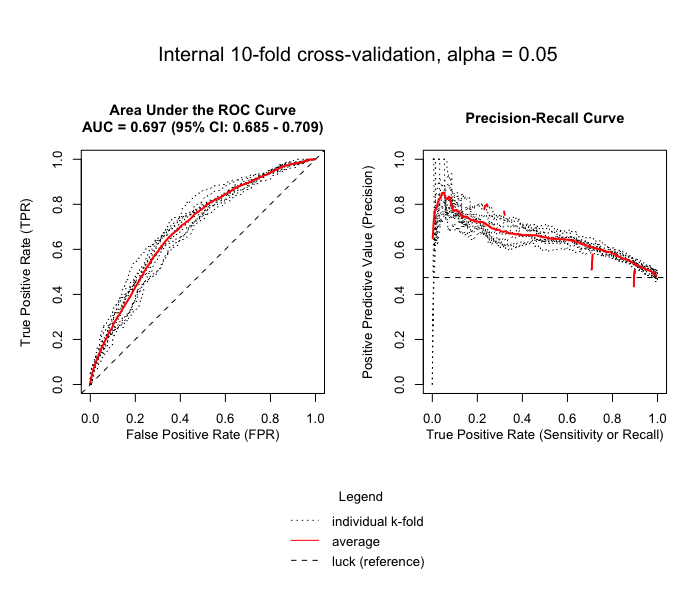
envi::plot_cv(test1)
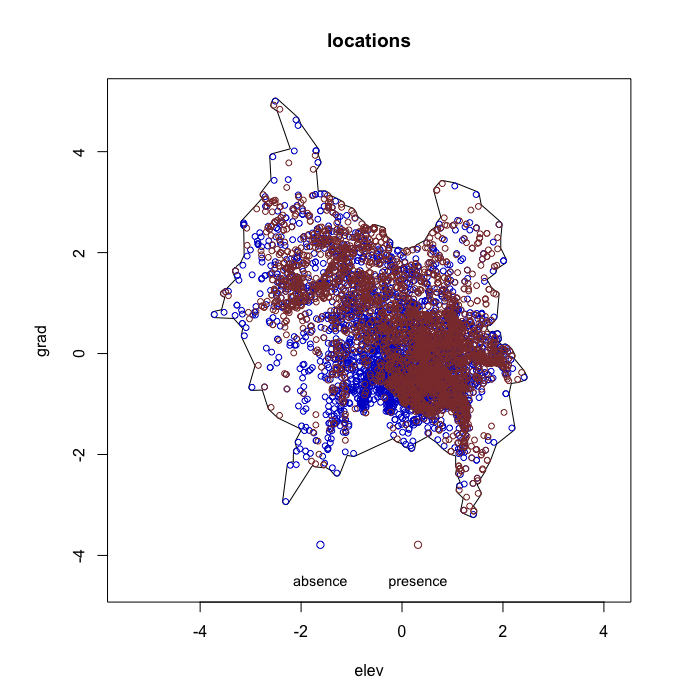
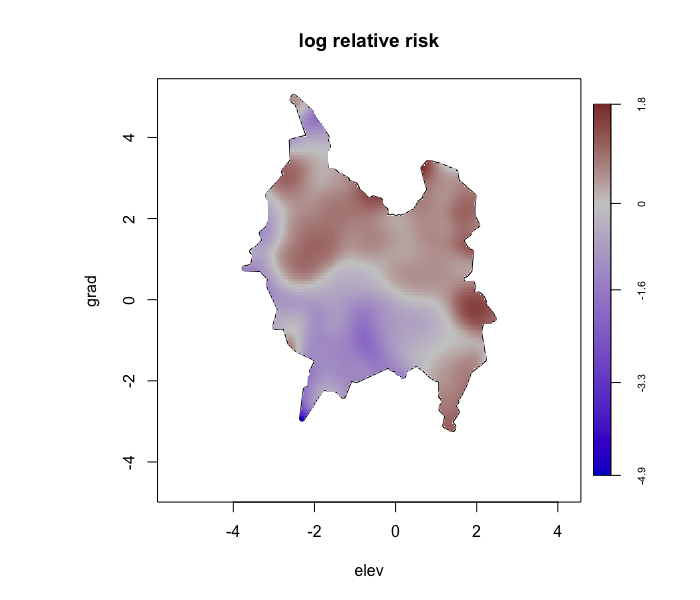
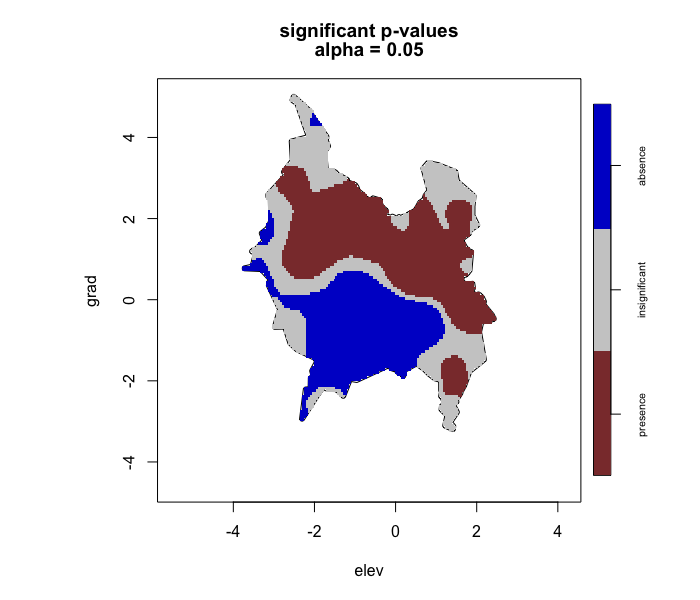
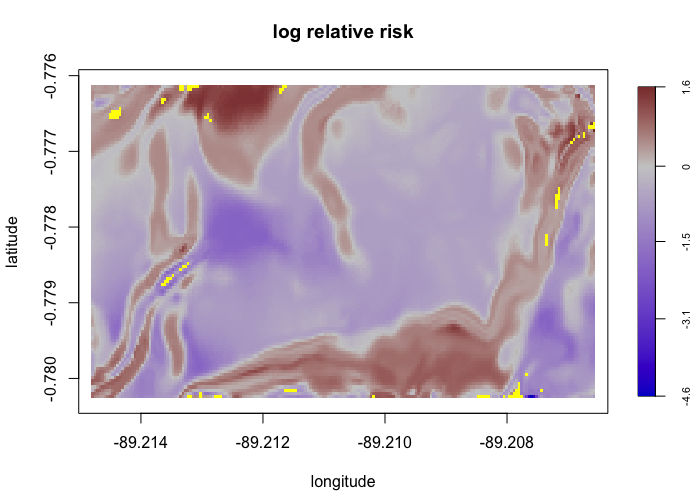
# -------------------------------------- #
# Run lrren() with Bonferroni correction #
# -------------------------------------- #
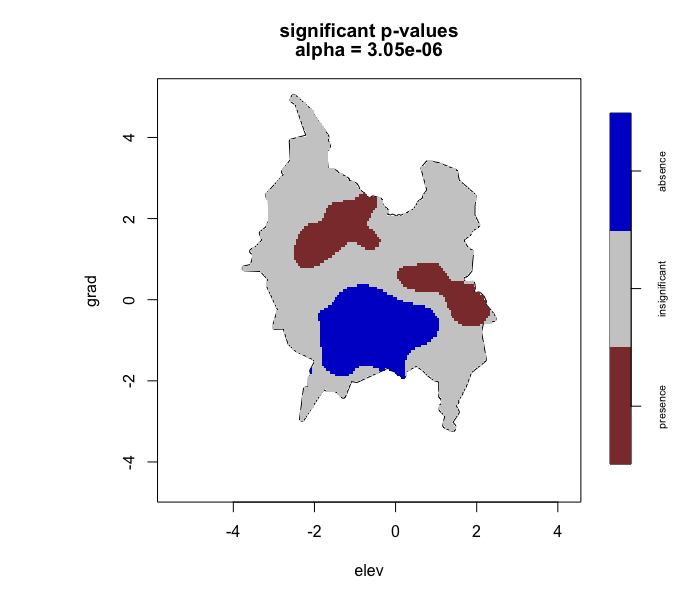
test2 <- envi::lrren(obs_locs = obs_locs,
predict_locs = predict_locs,
predict = TRUE,
p_correct = "Bonferroni")
# Note: Only showing third plot
envi::plot_obs(test2)
# Note: Only showing second plot
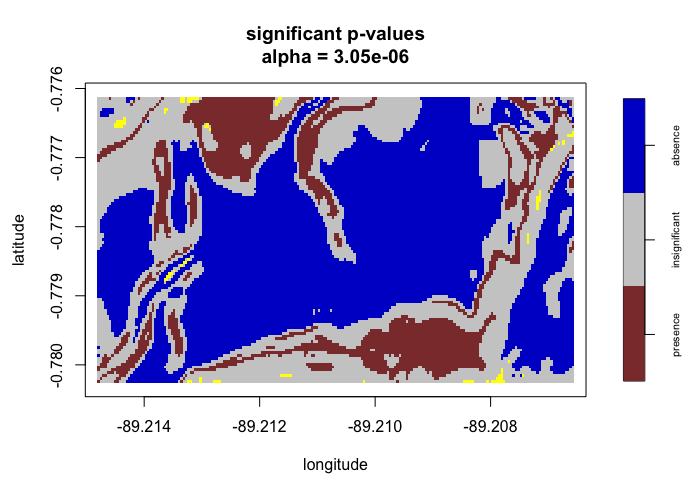
envi::plot_predict(test2,
cref0 = "EPSG:5472",
cref1 = "EPSG:4326")
# Note: plot_cv() will display the same results because cross-validation only performed for the log relative risk estimate
For the perlrren() function
set.seed(1234) # for reproducibility
# ------------------ #
# Necessary packages #
# ------------------ #
library(envi)
library(raster)
library(spatstat.data)
library(spatstat.geom)
library(spatstat.random)
# -------------- #
# Prepare inputs #
# -------------- #
# Using the 'bei' and 'bei.extra' data within {spatstat.data}
# Scale environmental covariates
ims <- spatstat.data::bei.extra
ims[[1]]$v <- scale(ims[[1]]$v)
ims[[2]]$v <- scale(ims[[2]]$v)
# Presence data
presence <- spatstat.data::bei
spatstat.geom::marks(presence) <- data.frame("presence" = rep(1, presence$n),
"lon" = presence$x,
"lat" = presence$y)
# (Pseudo-)Absence data
absence <- spatstat.random::rpoispp(0.008, win = ims[[1]])
spatstat.geom::marks(absence) <- data.frame("presence" = rep(0, absence$n),
"lon" = absence$x,
"lat" = absence$y)
# Combine and create 'id' and 'levels' features
obs_locs <- spatstat.geom::superimpose(presence, absence, check = FALSE)
spatstat.geom::marks(obs_locs)$id <- seq(1, obs_locs$n, 1)
spatstat.geom::marks(obs_locs)$levels <- as.factor(stats::rpois(obs_locs$n, lambda = 0.05))
spatstat.geom::marks(obs_locs) <- spatstat.geom::marks(obs_locs)[ , c(4, 2, 3, 1, 5)]
# -------------- #
# Run perlrren() #
# -------------- #
# Uncertainty in observation locations
## Most observations within 10 meters
## Some observations within 100 meters
## Few observations within 500 meters
test3 <- envi::perlrren(obs_ppp = obs_locs,
covariates = ims,
radii = c(10,100,500),
verbose = FALSE, # may not be availabe if parallel = TRUE
parallel = TRUE,
n_sim = 100)
# ------------------ #
# Run plot_perturb() #
# ------------------ #
envi::plot_perturb(test3,
cref0 = "EPSG:5472",
cref1 = "EPSG:4326",
cov_labs = c("elev", "grad"))